MESE veto methods¶
The MESE project comes with several methods for vetoing the background of atmospheric muon tracks.
Outer-layer veto¶
The outer part of IceCube is used as an active veto against atmospheric muons, similar to the one developed for the HESE analysis. The veto region consists of the DOMs on the outer strings of the detector, the top 90m of the detector, the bottommost active DOM on each string, and all DOMs between vertical depths of 2050m and 2170m. The top of the detector is measured from the first DOM on the deepest string.
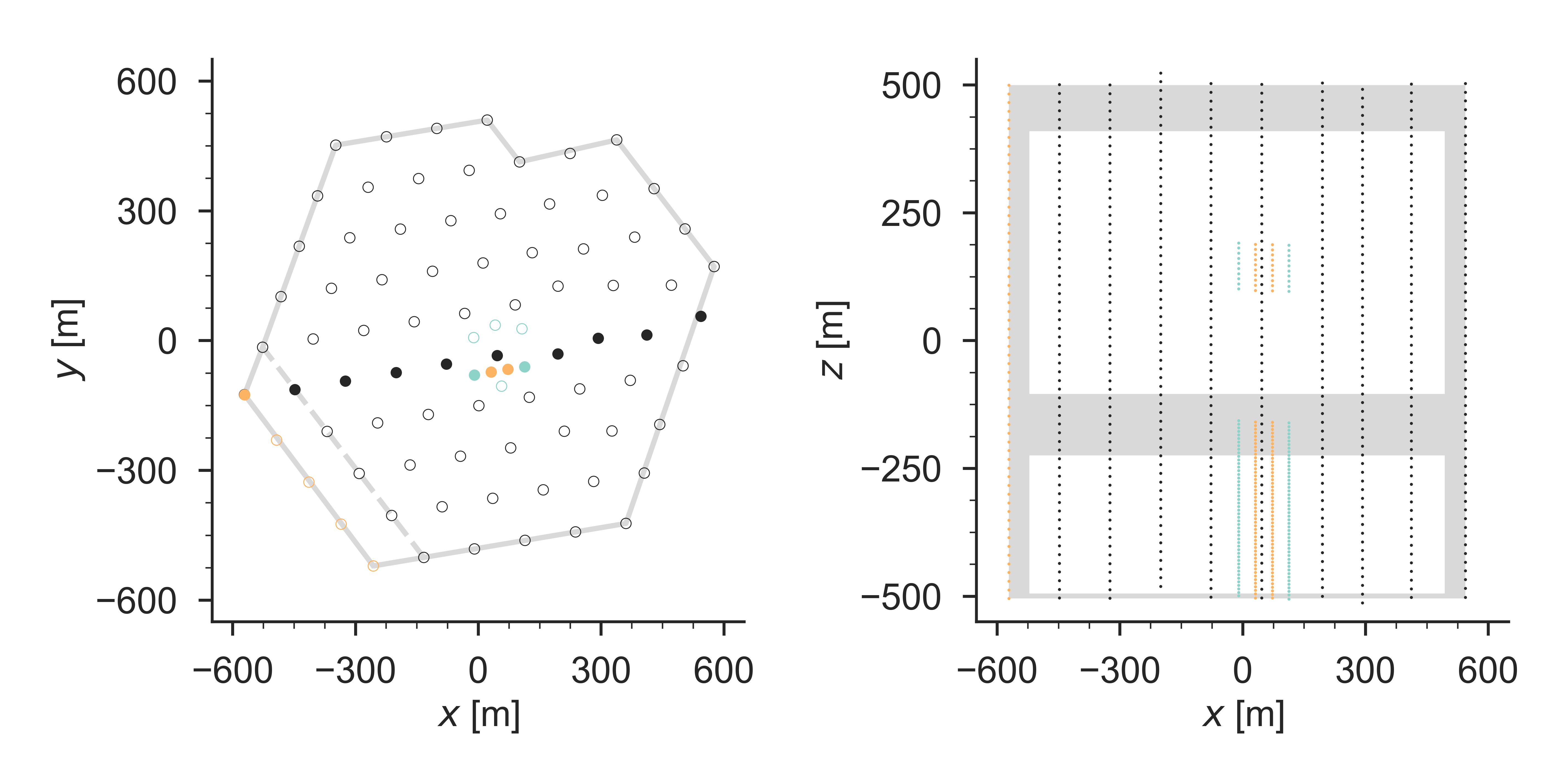
Left: top view on the IceCube geometry. Right: side view along the filled strings shown in the left plot. DeepCore strings are shown in turquoise. Strings colored in orange were not yet deployed in the IC79 configuration. The outer-layer veto is shown in gray.¶
Events that deposit charge in the veto region before a particular start time are removed. The start time is determined by sliding a time window of 3μs through all time-ordered HLC pulses detected on non-DeepCore DOMs until it contains a charge of
depending on the total charge \(q_\mathrm{tot}\) contained in this pulse series.
Down-going muon track veto¶
The remaining background is dominated by dim muons that pass the outer-layer veto undetected before suffering a large stochastic energy loss. This background is efficiently removed by the inner down-going track veto, which counts the HLC and SLC pulses that are not consistent with cascade-like emission at the reconstructed vertex position, but can be associated to a down-going muon track, going through the reconstructed vertex position. The direction of this track is determined in a scan of 104 equally spaced down-going directions, based on a HEALPix grid.
